工具链-Carla
官方文档:https://carla.readthedocs.io/en/0.9.9/#getting-started
Carla是一款开源的 自动驾驶 仿真器,它基本可以用来帮助训练自动驾驶的所有模块,包括感知系统,Localization,规划系统等等。许多自动驾驶公司在进行实际路跑前都要在这Carla上先进行训练。
1. 基本架构
Client-Server 的交互形式
Carla主要分为Server与Client两个模块
Server 端
基于 UnrealEnigne3D 渲染建立仿真世界。
Client 端
由用户控制,用来调整、变化仿真世界:不同时刻到底该如何运转(比如天气是什么样,有多少辆车在跑,速度是多少)。用户通过书写 Python/C++ 脚本来向 Server 端输送指令指导世界的变化,Server 根据用户的指令去执行。
另外,Client 端也可以接受 Server 端的信息,譬如某个照相机拍到的路面图片。
核心模块
Traffic Manager:
模拟类似现实世界负责的交通环境。通过这个模块,用户可以定义N多不同车型、不同行为模式、不同速度的车辆在路上与你的自动驾驶汽车(Ego-Vehicle)一起玩耍。
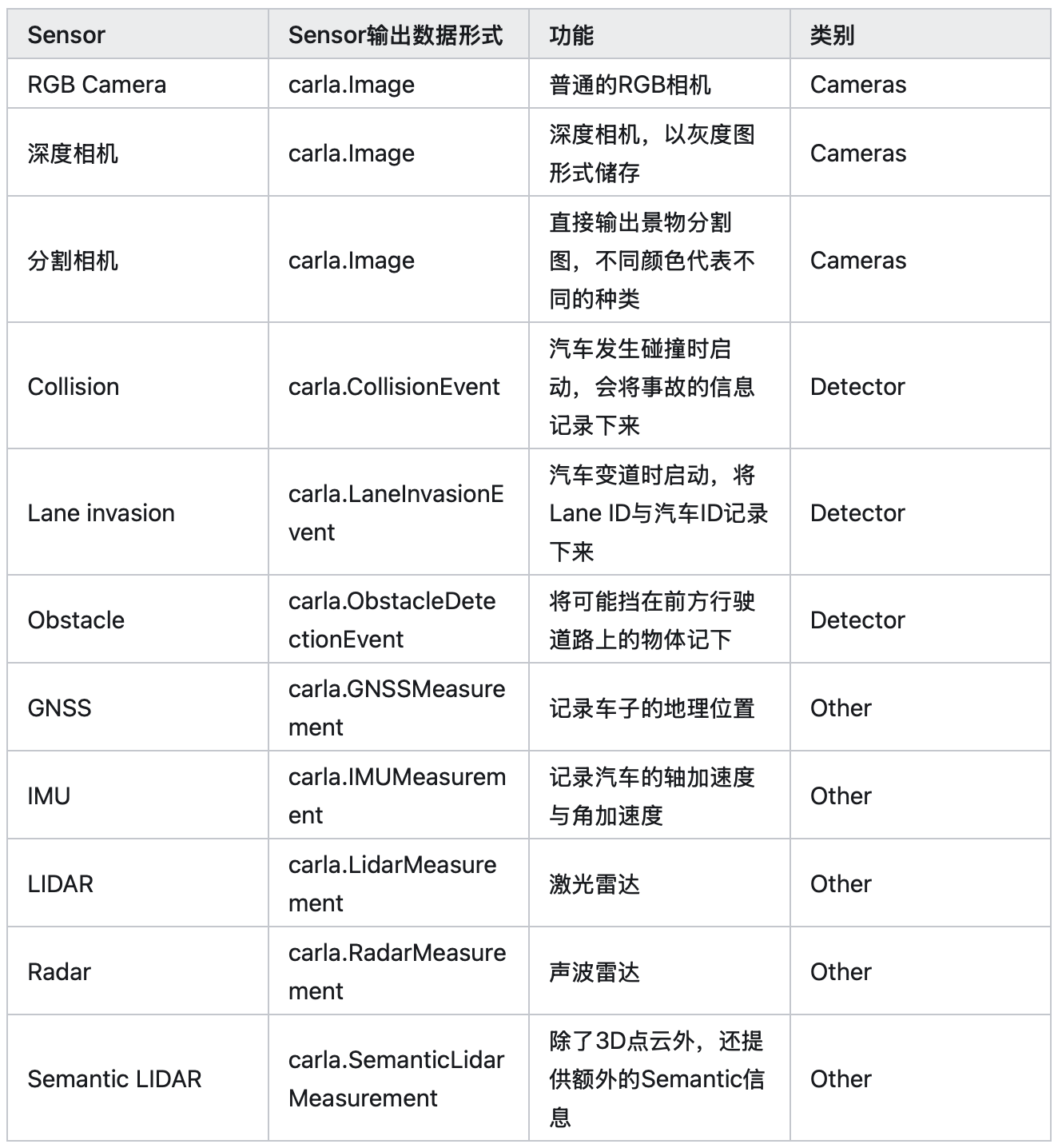
Sensors:
Carla 里面有各种各样模拟真实世界的传感器模型,包括相机、激光雷达、声波雷达、IMU、GNSS等等。为了让仿真更接近真实世界,它里面的相机拍出的照片甚至有畸变和动态模糊效果。用户一般将这些Sensor attach到不同的车辆上来收集各种数据。
Recorder:
该模块用来记录仿真每一个时刻(Step)的状态,可以用来回顾、复现等等。
ROS bridge:
该模块可以让 Carla 与 ROS、Autoware 交互,使得在仿真里测试自动驾驶系统变得可能。
Open Assest:
这个模块为仿真世界添加 customized 的物体库,比如可以在默认的汽车蓝图里再加一个真实世界不存在、外形酷炫的小飞汽车,用来给 Client 端调用。
2. API 使用
启动
./CarlaUE4.shClient and World
创建 Client,并且设置一个 timeout 时间防止连接时间过久。
# 其中2000是端口,2.0是秒数 client = carla.Client('localhost', 2000) client.set_timeout(2.0)通过构建的 Client 来获取仿真世界(World)。如果想让仿真世界有任何变化,都要对这个获取的world进行操作。
world = client.get_world()改变世界的天气
weather = carla.WeatherParameters(cloudiness=10.0, precipitation=10.0, fog_density=10.0) world.set_weather(weather)
Actor 与 Blueprint
Actor 是在仿真世界里则代表可以移动的物体,包括汽车,传感器(因为传感器要安在车身上)以及行人。
生成(spawn) Actor
如果想生成一个Actor, 必须要先定义它的蓝图(Blueprint)
# 拿到这个世界所有物体的蓝图 blueprint_library = world.get_blueprint_library() # 从浩瀚如海的蓝图中找到奔驰的蓝图 ego_vehicle_bp = blueprint_library.find('vehicle.mercedes-benz.coupe') # 给我们的车加上特定的颜色 ego_vehicle_bp.set_attribute('color', '0, 0, 0')构建好蓝图以后,下一步便是选定它的出生点。
可以给固定的位子,也可以赋予随机的位置,不过这个位置必须是空的位置,比如你不能将奔驰扔在一棵树上。
# 找到所有可以作为初始点的位置并随机选择一个 transform = random.choice(world.get_map().get_spawn_points()) # 在这个位置生成汽车 ego_vehicle = world.spawn_actor(ego_vehicle_bp, transform)操纵(Handling)Actor
汽车生成以后,便可以随意挪动它的初始位置,定义它的动态参数。
# 给它挪挪窝 location = ego_vehicle.get_location() location.x += 10.0 ego_vehicle.set_location(location) # 把它设置成自动驾驶模式 ego_vehicle.set_autopilot(True) # 我们可以甚至在中途将这辆车“冻住”,通过抹杀它的物理仿真 # actor.set_simulate_physics(False)注销(Destroy) Actor
当这个脚本运行完后要记得将这个汽车销毁掉,否则它会一直存在于仿真世界,可能影响其他脚本的运行。
# 如果注销单个Actor ego_vehicle.destroy() # 如果你有多个Actor 存在list里,想一起销毁。 client.apply_batch([carla.command.DestroyActor(x) for x in actor_list])
Sensor搭建
Camera构建
与汽车类似,我们先创建蓝图,再定义位置,然后再选择我们想要的汽车安装上去。不过,这里的位置都是相对汽车中心点的位置(以米计量)。
camera_bp = blueprint_library.find('sensor.camera.rgb') camera_transform = carla.Transform(carla.Location(x=1.5, z=2.4)) camera = world.spawn_actor(camera_bp, camera_transform, attach_to=ego_vehicle)再对相机定义它的 callback function,定义每次仿真世界里传感器数据传回来后,我们要对它进行什么样的处理。如,只简单地将文件存在硬盘里。
camera.listen(lambda image: image.save_to_disk(os.path.join(output_path, '%06d.png' % image.frame)))Lidar构建
Lidar 可以设置的参数比较多,现阶段设置一些常用参数即可。
lidar_bp = blueprint_library.find('sensor.lidar.ray_cast') lidar_bp.set_attribute('channels', str(32)) lidar_bp.set_attribute('points_per_second', str(90000)) lidar_bp.set_attribute('rotation_frequency', str(40)) lidar_bp.set_attribute('range', str(20))接着把 lidar 放置在奔驰上, 定义它的 callback function.
lidar_location = carla.Location(0, 0, 2) lidar_rotation = carla.Rotation(0, 0, 0) lidar_transform = carla.Transform(lidar_location, lidar_rotation) lidar = world.spawn_actor(lidar_bp, lidar_transform, attach_to=ego_vehicle) lidar.listen(lambda point_cloud: \ point_cloud.save_to_disk(os.path.join(output_path, '%06d.ply' % point_cloud.frame)))
观察者(spectator)放置
观察仿真界面时,自己的视野并不会随我们造的小车子移动,所以经常会跟丢它。
解决办法:把 spectator 对准汽车,这样小汽车就永远在我们的视野里了。
spectator = world.get_spectator() transform = ego_vehicle.get_transform() spectator.set_transform(carla.Transform(transform.location + carla.Location(z=20), carla.Rotation(pitch=-90)))查看储存的照片与3D点云
查看点云图需要另外安装 meshlab, 然后进入 meshlab 后选择 import mesh:
sudo apt-get update -y sudo apt-get install -y meshlab meshlab
3. 同步模式
问题:储存的相机照片有严重的掉帧现象
仿真server默认为异步模式,它会尽可能快地进行仿真,而不管客户是否跟上了它的步伐
仿真世界里的时间步长:一个 time-step 相当于仿真世界进行了一次更新(比如小车们又往前挪了一小步,天气变阴了一丢丢)。分为 Variable time-step 和 Fixed time-step。
异步模式:Variable time-step
仿真每次步长所需要的真实时间是不一定的,可能这一步用了3ms, 下一步用了5ms, 但是它会竭尽所能地快速运行。这是仿真默认的模式:
settings = world.get_settings() settings.fixed_delta_seconds = None # Set a variable time-step world.apply_settings(settings)在异步模式下, server会自个跑自个的,client需要跟随它的脚步,如果client过慢,可能导致server跑了三次,client才跑完一次, 这就是为什么照相机储存的照片会掉帧的原因。
同步模式:Fixed time-step
在这种时间步长设置下,每次time-step所消耗的时间是固定的,比如永远是5ms. 设置代码如下:
settings = world.get_settings() settings.fixed_delta_seconds = 0.05 #20 fps, 5ms world.apply_settings(settings)在同步模式下,simulation会等待客户完成手头的工作后,再进行下一次更新。
4. 交通管理器
Traffic Manager 简称TM,是仿真里用来控制车辆行为的模块。纯C++构造包装被Python调用的:~/carla/Libcarla/source/trafficmanager/TrafficManager.h
Traffic Manager的内部架构
实践
0 预备
下载 carla
Get Python from anaconda.com
Create virtual environment
launch anaconda prompt
conda create –name carla-sim python=3.7
activate carla-sim
Install additional libraries via “pip install”:
- pip install carla, pygame, numpy, jupyter and opencv-python
1 基本构件块
# all imports
import carla # the sim Library itself
import random # to pick random spawn point
import cv2 # to work with images from cameras
import numpy as np # in this example to change image representation - re-shaping
# connect to the sim
client = carla.Client('localhost', 2000)
# optional to Load different towns
client.load_world('Towne5')
# define environment/world and get possible places to spawn a car
world = client.get_world()
spawn_points = world.get_map().get_spawn_points()
# Look for a blueprint of Mini car,得到很多名为"mini"的汽车实例
vehicle_bp = world.get_blueprint_library().filter('*mini*')
# spawn a car in a random location
start_point = random.choice(spawn_points)
vehicle = world.try_spawn_actor(vehicle_bp[0], start_point)
# move simulator view to the car
spectator = world.get_spectator()
start_point.location.z = start_point.location.z+1 #start_point was used to spawn
spectator.set_transform(start_point)
#send the car off on autopilot - this will leave the spectator
vehicle.set_autopilot(True)
2 在汽车上设置摄像头
#setting RGB Camera - this follow the approach explained in a Carla video
# Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=om8kLsBj4rc&t=1184s
#camera mount offset on the car - you can tweak these to each car to avoid any p
CAMERA_POS_Z = 1.6 # this means 1.6m up from the ground
CAMERA_POS_X = 0.9 # this is 0.9m forward
camera_op = world.get_blueprint_library().find('sensor.camera.rgb')
camera_bp.set_attribute('image_size_x', '640') # this ratio works in CARLA 9.14
camera_bp.set_attribute('image_size_y', '360')
camera_init_trans = carla.Transform(carla.Location(z=CAMERA_POS_Z, x=CAMERA_POS_X))
# this creates the camera in the sim
camera = world.spawn_actor(camera_bp, camera_init_trans, attach_to=vehicle)
def camera_callback(image, data _dict):
data_dict['image'] = np.reshape(np.copy(image.raw_data), (image.height, image.width, 4))
image_w = camera_bp.get_attribute('image_size_x') .as_int()
image_h = camera_bp.get_attribute('image_size_y').as_int()
camera_data = {'image': np.zeros ((image_h, image_w,4))}
# this actually opens a live stream from the camera
camera.listen(lambda image: camera_callback(image, camera_data))
# grab a snapshot from the camera an show in a pop-up window
img = camera_data['image']
cv2.imshow('RGB Camera', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
Output: -1
# clean up after yourself
camera.stop() # this is the opposite of camera.listen
for actor in world.get_actors().filter('*vehicle*'):
actor.destroy()
for sensor in world.get_actors().filter('*sensor*'):
sensor.destroy()
3 控制汽车
速度和油门踏板
'''
This is the new Bit for tutorial 4
First we need to create controls functions so we could
push the car along the route
'''
# define speed contstants
PREFERRED_SPEED = 20 # what it says
SPEED_THRESHOLD = 2 # defines when we get close to desired speed so we drop the
# adding params to display text to image
font = CV2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
# org - defining lines to display telemetry values on the screen
org = (30, 30) # this Line will be used to show current speed
org2 = (30, 50) # this Line will be used for future steering angle
org3 = (30, 70) # and another line for future telemetry outputs
fontScale = 0.5
# white color
color = (255, 255, 255)
# line thickness of 2 px
thickness = 1
def maintain_ speed(s):
'''
this is a very simple function to maintan desired speed s arg is actual current speed
'''
if 5 >= PREFERRED_SPEED:
return 0
elif s < PREFERRED_SPEED - SPEED_THRESHOLD:
return 0.8 # think of it as % of "full gas"
else:
return 0.4 # tweak this if the car is way over or under preferred speed
# now Little demo to drive straight
# close to a desired speed
# - press l to exit, you need to run the bit above to start the car
cv2.namedWindow('RGB Camera', CV2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)
cv2.imshow('RGB Camera', camera_data['image'])
# main Loop
quit = False
while True:
# Carla Tick
world.tick()
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):
quit = True
break
image = camera_data['image']
steering_angle = 0 # we do not have it yet
# to get speed we need to use 'get velocity' function
v = vehicle.get_velocity()
# if velocity is a vector in 3d
# then speed is like hypothenuse in a right triangle
# and 3.6 is a conversion factor from meters per second to kmh
# e.g. mh is 1000 meters and one hour is 60 min with 60 sec = 3600 sec
speed = round(3.6 * math.sqrt(v.x**2 + v.y**2 + v.z**2),0)
# now we add the speed to the window showing a camera mounted on the car
image = cv2. putText (image, 'Speed: '+str(int(speed))+' kmh', org2,
font, fontScale, color, thickness, cv2. LINE_AA)
# this is where we used the function above to determine accelerator input
# from current speed
estimated_throttle = maintain_speed (speed)
# now we apply accelerator
vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=estimated_throttle,
steer=steering_angle))
cv2. imshow('RGB Camera', image)
#clean up
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
camera.stop()
for actor in world.get_actors().filter('*vehicle*'):
actor.destroy()
for sensor in world.get_actors().filter ('*sensor*'):
sensor.destroy()
转向角度
- 汽车当前位置
- 汽车想去的位置
- 汽车当前角度
# test steering function
world = client.get_world()
spawn_points = world.get_map().get_spawn_points()
# look for a blueprint of Mini car
vehicle_bp = world.get_blueprint_library().filter('*mini*')
start_point = spawn_points[0]
vehicle = world.try_spawn_actor(vehicle_bp[0], start_point)
# setting RGB Camera - this follow the approach explained in a Carla video
# link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=om8klsBj4rc&t=1184s
# camera mount offset on the car - you can tweak these to have the car in view or not
CAMERA_POS_Z = 3
CAMERA_POS_X = -5
camera_bp = world.get_blueprint_library().find('sensor.camera.rgb')
camera_bp.set_attribute('image_size_x', '640') # this ratio works in CARLA 9.14 on Windows
camera_bp.set_attribute('image_size_y', '360')
camera_init_trans = carla.Transform(carla.Location(z=CAMERA_POS_Z,x=CAMERA_POS_X))
# this creates the camera in the sim
camera = world.spawn_actor(camera_bp,camera_init_trans,attach_to=vehicle)
def camera_callback(image,data_dict):
data_dict['image'] = np.reshape(np.copy(image.raw_data),(image.height,image.width,4))
image_w = camera_bp.get_attribute('image_size_x').as_int()
image_h = camera_bp.get_attribute('image_size_y').as_int()
camera_data = {'image': np.zeros((image_h,image_w,4))}
# this actually opens a live stream from the camera
camera.listen(lambda image: camera_callback(image,camera_data))
cv2.namedWindow('RGB Camera',cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)
cv2.imshow('RGB Camera',camera_data['image'])
# main loop
quit = False
curr_wp = 5 # we will be tracking waypoints in the route and switch to next one wen we get close to current one
predicted_angle = 0
while curr_wp<len(route)-1:
# Carla Tick
world.tick()
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):
quit = True
vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=0,steer=0,brake=1))
break
image = camera_data['image']
while curr_wp<len(route) and vehicle.get_transform().location.distance(route[curr_wp][0].transform.location)<5:
curr_wp +=1 # move to next wp if we are too close
predicted_angle = get_angle(vehicle,route[curr_wp][0])
image = cv2.putText(image, 'Steering angle: '+str(round(predicted_angle,3)), org, font, fontScale, color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)
v = vehicle.get_velocity()
speed = round(3.6 * math.sqrt(v.x**2 + v.y**2 + v.z**2),0)
image = cv2.putText(image, 'Speed: '+str(int(speed)), org2, font, fontScale, color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)
image = cv2.putText(image, 'Next wp: '+str(curr_wp), org3, font, fontScale, color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)
estimated_throttle = maintain_speed(speed)
# extra checks on predicted angle when values close to 360 degrees are returned
if predicted_angle<-300:
predicted_angle = predicted_angle+360
elif predicted_angle > 300:
predicted_angle = predicted_angle -360
steer_input = predicted_angle
# and conversion of to -1 to +1
if predicted_angle<-40:
steer_input = -40
elif predicted_angle>40:
steer_input = 40
# conversion from degrees to -1 to +1 input for apply control function
steer_input = steer_input/75
vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=estimated_throttle, steer=steer_input))
cv2.imshow('RGB Camera',image)
# clean up
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
camera.stop()
for sensor in world.get_actors().filter('*sensor*'):
sensor.destroy()
vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=0,steer=0,brake=1))
定位汽车
import carla
client = carla.Client('localhost', 2000)
world = client.get_world()
spawn_points = world.get_map().get_spawn_points()
vehicle_bp = world.get_blueprint_library().filter('*firetruck*')
start_point = spawn_points[0]
vehicle = world.try_spawn_actor(vehicle_bp[0], start_point)
# get the car's position on the map
vehicle_pos = vehicle.get_transform()
print(vehicle_pos)
Transform(Location(x=-64.644844, y=24.472013, z=-0.001559), Rotation(pitch=-0.000061, yaw=0.159197, roll=0.000632))
# initial spawn point is the same - just 0.6m higher off the ground
print(start_point)
Transform (Location (x=-64.644844, y=24.471010, z=0.600000), Rotation(pitch=0.000000, yaw=0.159198, roll=0.000000))
# send vehicle off
vehicle.set_autopilot(True)
# get actual position from the car moving
vehicle_pos = vehicle.get_transform()
print(vehicle_pos)
Transform (Location(x=-114.478943, y=65.782814, z=-0.003669), Rotation(pitch=0.000997, yaw=90.641518, roll=0.000133))
# now look at the map
town_map = world.get_map()
type (town_map)
Output: carla.libcarla.Map