「算法模版」树
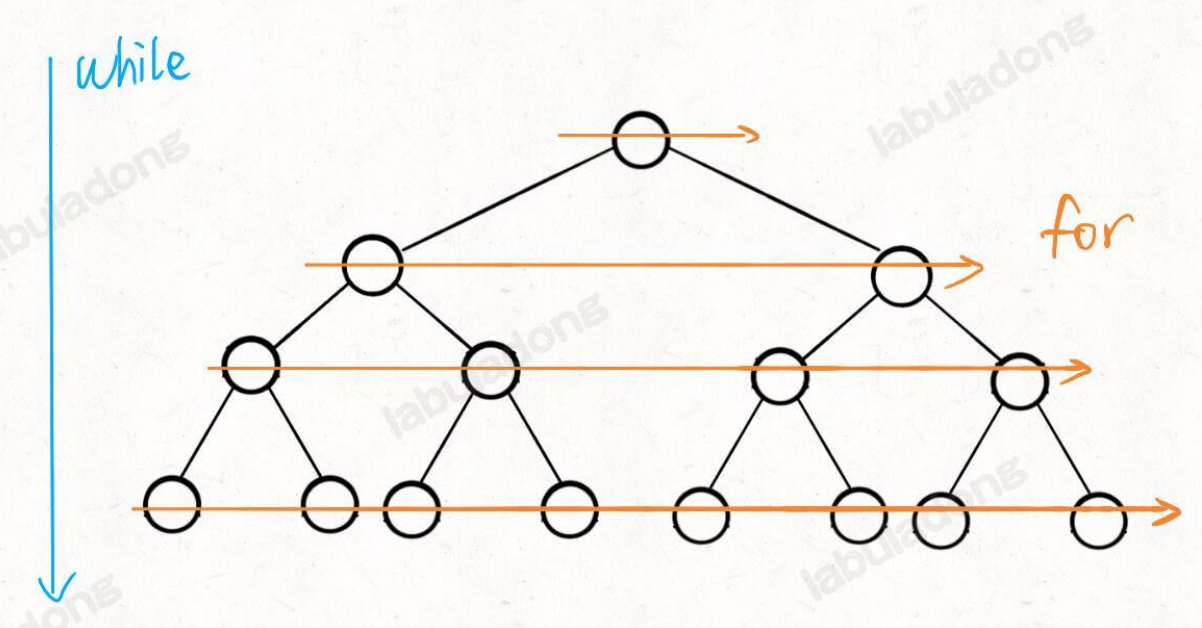
层级遍历
while 循环控制⼀层⼀层往下⾛,for 循环利⽤ sz 变量控制从左到右遍历每⼀层⼆叉树节点。
// 输⼊⼀棵⼆叉树的根节点,层序遍历这棵⼆叉树
void levelTraverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.push(root);
int depth = 1;
// 从上到下遍历⼆叉树的每⼀层
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int sz = q.size();
// 从左到右遍历每⼀层的每个节点
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
TreeNode cur = q.poll();
printf("节点 %s 在第 %s 层", cur, depth);
// 将下⼀层节点放⼊队列
if (cur.left != null) {
q.push(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
q.offer(cur.right);
}
}
depth++;
}
}
BFS
⽤了⼀个 visited 集合记录⾛过的节点,防⽌⾛回头路
每次从队列中拿出节点 cur 的时候,从 start 到 cur 的最短权重就是 step 记录的步数
// 输⼊起点,进⾏ BFS 搜索
int BFS(Node start) {
queue<Node> q; // 核⼼数据结构
set<Node> visited; // 避免⾛回头路
q.push(start); // 将起点加⼊队列
visited.add(start);
int step = 0; // 记录搜索的步数
while (q not empty) {
int sz = q.size(); // 记录当前队列 q 中节点的数量size
/* 将当前队列中的所有节点向四周扩散⼀步 */
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
Node* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
printf("从 %s 到 %s 的最短距离是 %s", start, cur, step);
/* 将 cur 的相邻节点加⼊队列 */
for (Node x : cur.adj()) {
if (x not in visited) {
q.push(x);
visited.add(x);
}
}
}
step++;
}
return step; // 返回步数
}